Java的IO类体系庞大,初学者很容易迷失在其中。而解决这个问题的最好办法就是分门别类、各个击破。这里来介绍Java IO中关于文件IO一些常用类的具体用法
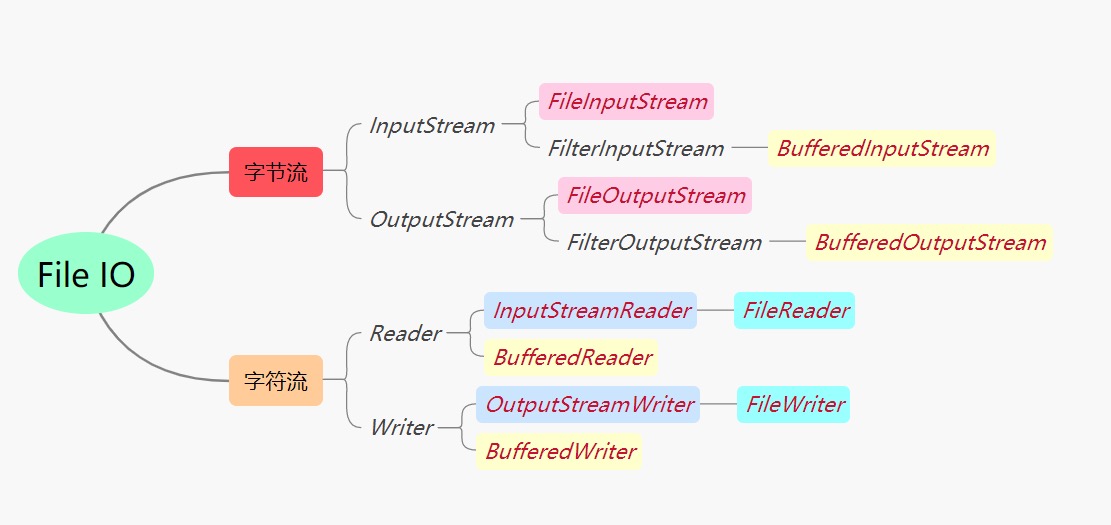
概述
上图中红字标识的10个IO类,是我们操作文件IO的常用类。乍一看会觉得很多,其实在我们理解了它们各自的作用再来看,会发现其实还是很清晰的。Java IO中可划分为两大类:字节流、字符流。前者以字节为单位进行操作,而后者则以字符为单位进行操作。所以如果是非文本类型文件(如图像)使用前者进行操作;而对于文本类型的文件更推荐通过后者进行操作。具体地,字节流可通过FileInputStream、FileOutputStream类进行构造获得。而对于字符流,一方面可通过转换流InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter将字节流转换为字符流来获得,另一方面其还可以直接通过FileReader、FileWriter来获得字符流(字符编码使用UTF-8)。更进一步地,Java为了提高IO的操作效率,还为字节流、字符流提供了相应的缓冲流:BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
字节流
具体地,字节流可分为输入流、输出流两种。对于输入字节流而言,其在抽象类InputStream中提供、定义了一组通用的操作方法,以供其子类来继承、实现。我们在了解这些方法的功用之后,就可以知道如何来操作其下具体的实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public abstract class InputStream implements Closeable {
...
public int available() throws IOException;
public abstract int read() throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
public void close() throws IOException;
...
}
|
对于输出字节流而言。其同样在抽象类OutputStream中提供、定义了一组通用的操作方法,以供其子类来继承、实现。我们在了解这些方法的功用之后,就可以知道如何来操作其下具体的实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public abstract class OutputStream implements Closeable, Flushable {
public void flush() throws IOException;
public abstract void write(int b) throws IOException;
public void write(byte b[]) throws IOException;
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
public void close() throws IOException;
}
|
1. FileInputStream 文件输入字节流
文件字节输入流FileInputStream是我们读取文件的具体类,其具体用法如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public static void testFileInputStream() throws Exception {
String file = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOStreamTest\\r1.txt";
FileInputStream in = null;
in = new FileInputStream(file);
int ch = -1;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while ( (ch=in.read()) != -1 ) {
sb.append((char) ch);
}
in.close();
System.out.println("str1: " + sb.toString());
in = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[4];
int count = 0;
String str = "";
while( (count=in.read(bytes)) != -1) {
String temp = new String(bytes, 0, count);
str += temp;
}
in.close();
System.out.println("str2: " + str);
}
|
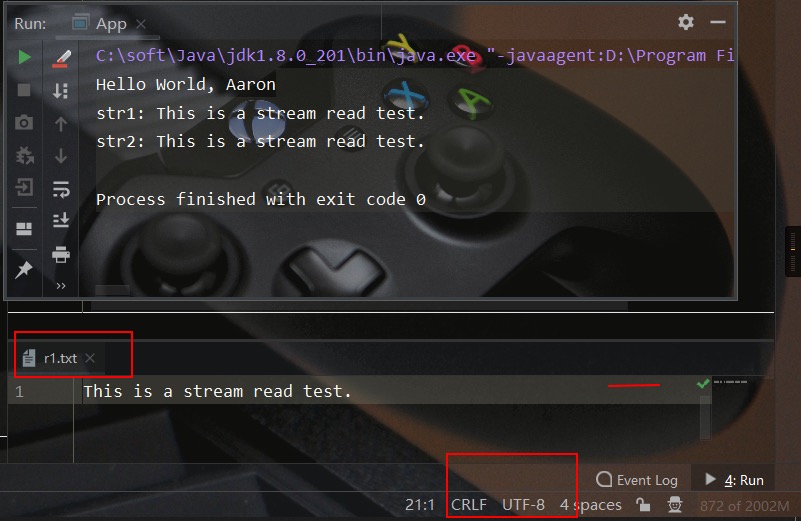
测试文件、测试结果如下所示:
2. FileOutputStream 文件输出字节流
文件输出字节流FileOutputStream是我们写入文件的具体类,其具体用法如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public static void testFileOutputStream() throws Exception {
String file1 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOStreamTest\\w1.txt";
String file2 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOStreamTest\\w2.txt";
String str = "字节流写测试";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
FileOutputStream out1 = new FileOutputStream(file1);
for(byte b : bytes ) {
out1.write(b);
}
out1.flush();
out1.close();
FileOutputStream out2 = new FileOutputStream(file2);
for(int i=0; i<bytes.length; i++) {
int s = i;
int e = i+4>=bytes.length ? bytes.length-1 : i+4;
int length = e - s + 1;
out2.write(bytes,s, length);
i = e;
}
out2.flush();
out2.close();
}
|
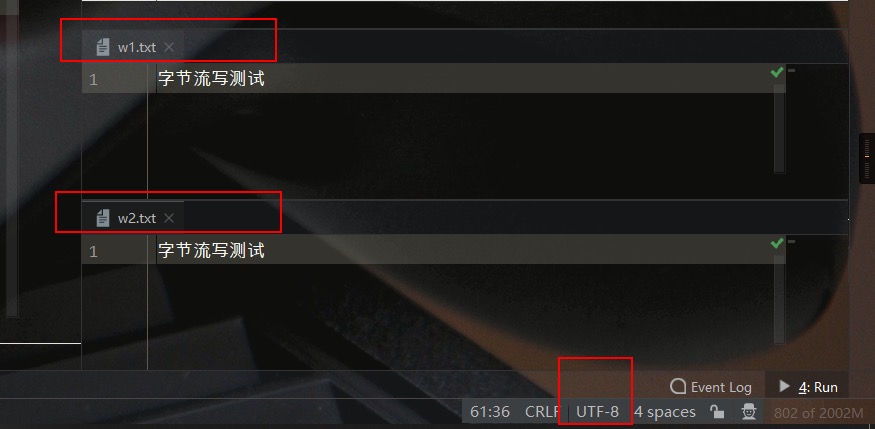
测试结果如下所示:
由于FileInputStream、FileOutputStream的每一次IO操作都是直接访问磁盘,我们知道磁盘的IO操作速度低于内存。为此Java提供了输入缓冲流BufferedOutputStream来将字节输出流的多次写入的数据结果先存于内存当中,待缓冲区满后再一次性全部写入到磁盘中,BufferedInputStream的作用同理
1. BufferedInputStream 输入缓冲字节流
我们需要先构造字节输入流,然后依此来构造输入缓冲字节流BufferedInputStream。其具体用法如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public static void testBufferedInputStream() throws Exception{
String file = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOBufferTest\\r1.txt";
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(in);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int count = -1;
String str = "";
while ((count = bufferedInputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
String temp = new String(buffer,0,count);
str += temp;
}
System.out.println("str: " + str);
bufferedInputStream.close();
}
|
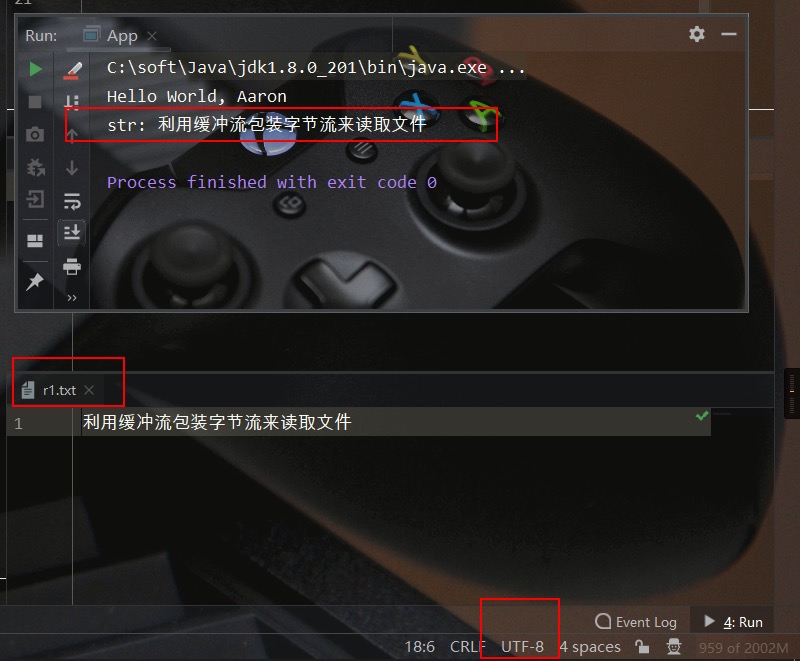
测试文件、测试结果如下所示:
2. BufferedOutputStream 输出缓冲字节流
我们需要先构造字节输出流,然后依此来构造输出缓冲字节流BufferedOutputStream。其具体用法如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public static void testBufferedOutputStream() throws Exception{
String file = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOBufferTest\\w1.txt";
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
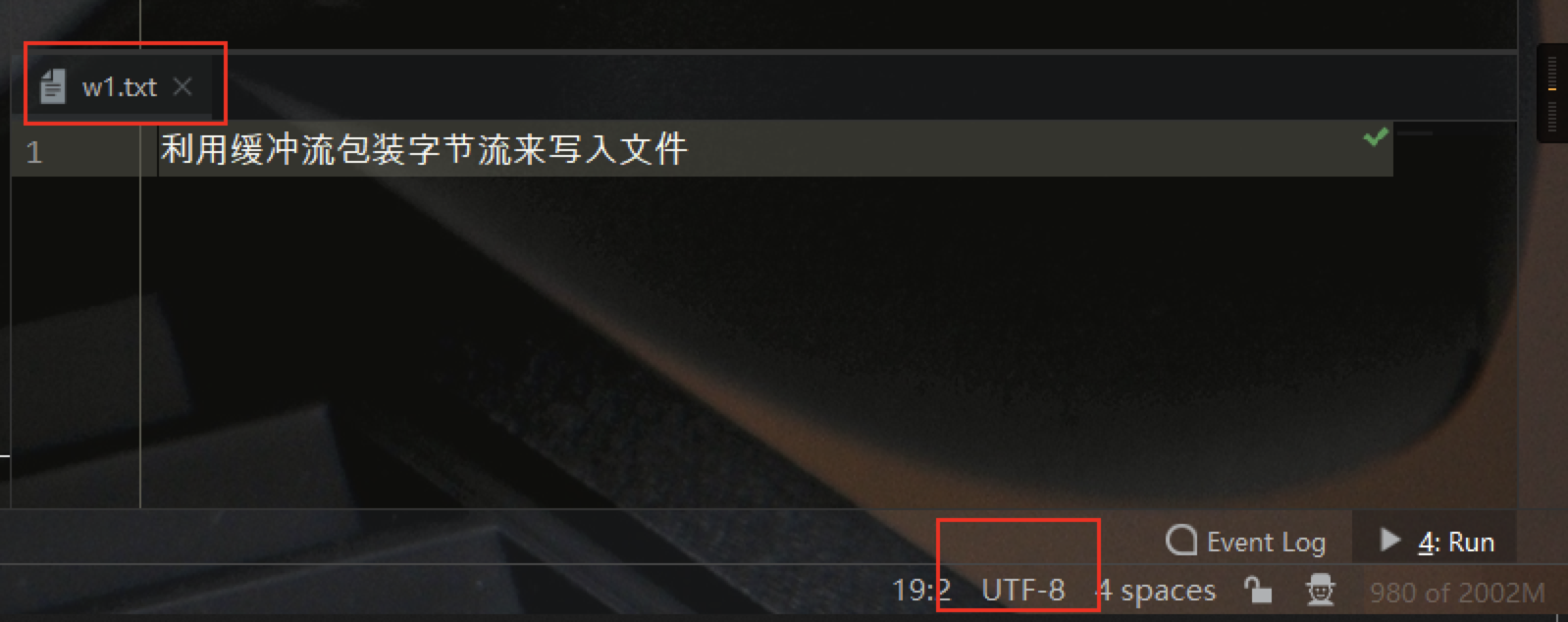
String str = "利用缓冲流包装字节流来写入文件";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
bufferedOutputStream.write(bytes);
bufferedOutputStream.flush();
bufferedOutputStream.close();
}
|
测试结果如下所示:
字符流
Reader、Writer 输入、输出字符流抽象类
同样地,字符流亦可分为输入流、输出流两种。对于输入字符流而言,其在抽象类Reader中提供、定义了一组通用的操作方法,以供其子类来继承、实现。我们在了解这些方法的功用之后,就可以知道如何来操作其下具体的实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public abstract class Reader implements Readable, Closeable {
...
public int read() throws IOException;
public int read(char cbuf[]) throws IOException;
abstract public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
abstract public void close() throws IOException;
...
}
|
类似地,字符流也有一个抽象类Writer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public abstract class Writer implements Appendable, Closeable, Flushable {
...
abstract public void flush() throws IOException;
public void write(int c) throws IOException;
public void write(char cbuf[]) throws IOException;
abstract public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
public void write(String str) throws IOException;
abstract public void close() throws IOException;
...
}
|
1. InputStreamReader 输入转换流
输入转换流InputStreamReader可以按将输入字节流转换为指定编码方式的输入字符流,其具体用法如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| public static void testReaderByInputStreamReader() throws Exception {
String file = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOStreamAndReaderWriterTest\\r1.txt";
FileInputStream in = null;
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = null;
in = new FileInputStream(file);
inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(in, "gbk");
int ch = -1;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while( (ch=inputStreamReader.read()) != -1 ) {
sb.append((char)ch);
}
inputStreamReader.close();
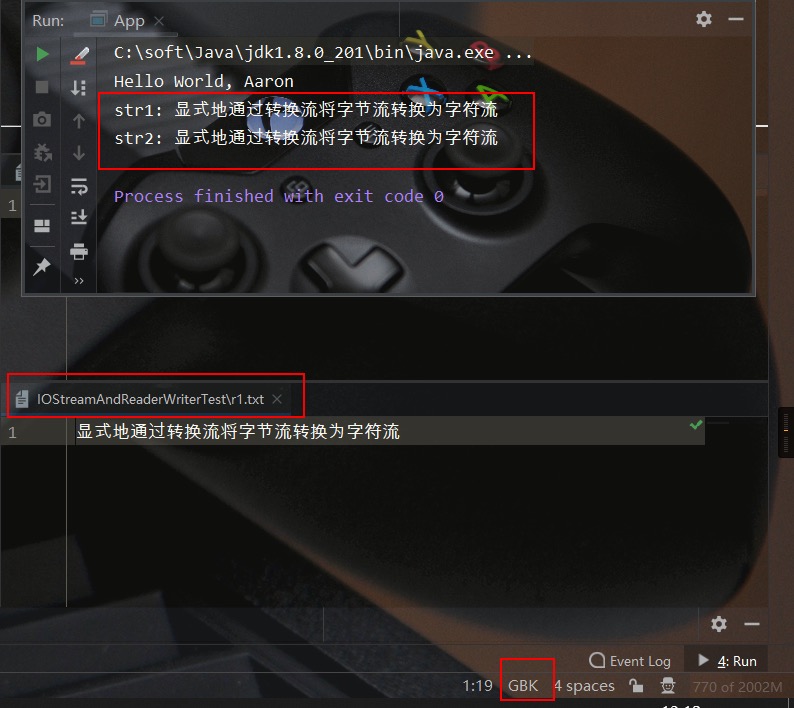
System.out.println("str1: " + sb.toString());
in = new FileInputStream(file);
inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(in, "gbk");
char[] chars = new char[4];
int counts = -1;
String str = "";
while ( (counts=inputStreamReader.read(chars))!= -1 ) {
String temp = new String(chars, 0, counts);
str += temp;
}
inputStreamReader.close();
System.out.println("str2: " + str);
}
|
测试文件、测试结果如下所示:
2. OutputStreamWriter 输出转换流
输出转换流OutputStreamWriter可以按将输出字节流转换为指定编码方式的输出字符流,其具体用法如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| public static void testWriterByOutputStreamWriter() throws Exception {
String file1 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOStreamAndReaderWriterTest\\w1.txt";
String file2 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOStreamAndReaderWriterTest\\w2.txt";
String file3 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOStreamAndReaderWriterTest\\w3.txt";
FileOutputStream out = null;
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = null;
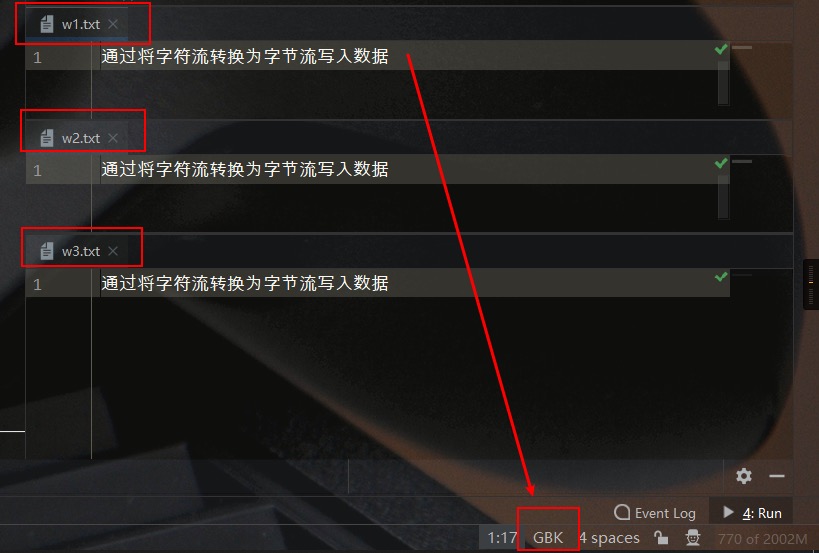
String str = "通过将字符流转换为字节流写入数据";
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
out = new FileOutputStream(file1);
outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "gbk");
for(char ch : chars) {
outputStreamWriter.write(ch);
}
outputStreamWriter.flush();
outputStreamWriter.close();
out = new FileOutputStream(file2);
outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "gbk");
outputStreamWriter.write(chars);
outputStreamWriter.flush();
out.close();
outputStreamWriter.close();
out = new FileOutputStream(file3);
outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "utf-8");
outputStreamWriter.write(str);
outputStreamWriter.flush();
outputStreamWriter.close();
}
|
测试结果如下所示:
FileReader、FileWriter 文件输入、输出字符流
前面提到的字符流是利用转换流来将字节流转换为字符流的,Java还分别提供了输入、输出转换流的子类FileReader、FileWriter文件输入、输出字符流,通过它们可以直接创建字符流。当然在FileReader、FileWriter的内部还是通过先创建字节流再利用UTF-8编码和转换流来生成字符流的。所以说,如果我们的文件编码是UTF-8的话,可以直接使用FileReader、FileWriter文件输入、输出字符流来创建字符流
1. FileReader 文件输入字符流
这里使用FileReader类创建输入字符流直接读取文件,其具体用法如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| public static void testReader() throws Exception {
String file = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOFileReaderWriter\\r1.txt";
FileReader reader = null;
reader = new FileReader(file);
int ch = -1;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while( (ch=reader.read()) != -1 ) {
sb.append( (char)ch );
}
reader.close();
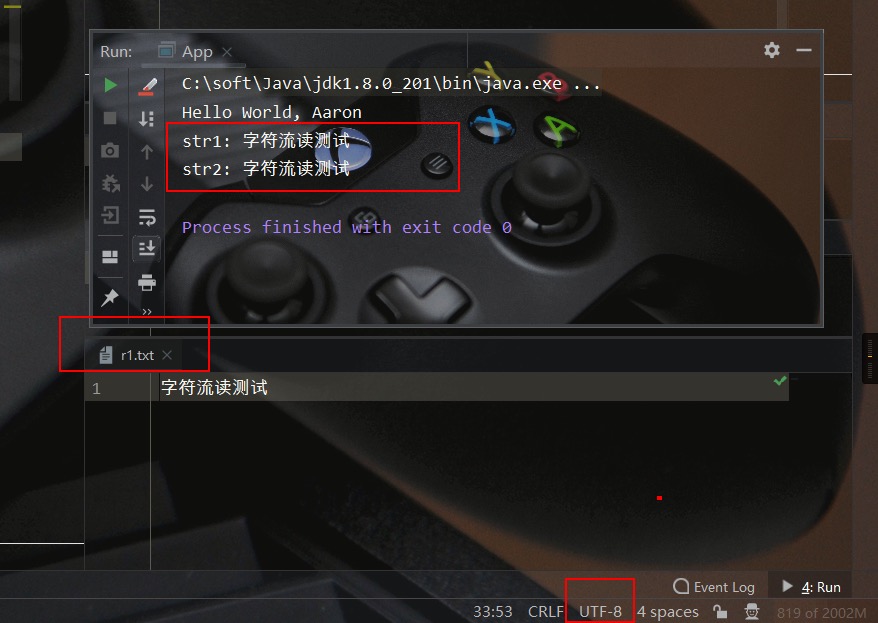
System.out.println("str1: " + sb.toString());
reader = new FileReader(file);
char[] chars = new char[4];
int counts = -1;
String str = "";
while ( (counts=reader.read(chars))!= -1 ) {
String temp = new String(chars, 0, counts);
str += temp;
}
reader.close();
System.out.println("str2: " + str);
}
|
测试文件、测试结果如下所示:
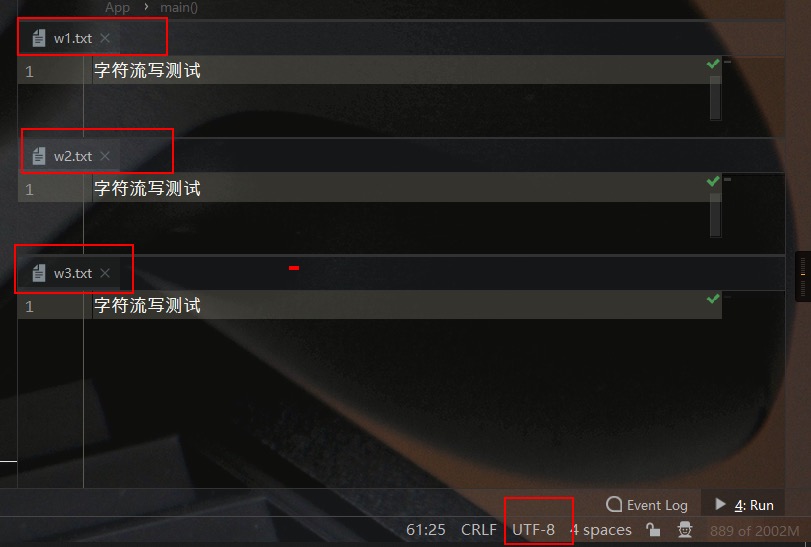
2. FileWriter 文件输出字符流
这里使用FileWriter类创建输出字符流直接写文件,其具体用法如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| public static void testWriter() throws IOException {
String file1 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOFileReaderWriter\\w1.txt";
String file2 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOFileReaderWriter\\w2.txt";
String file3 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOFileReaderWriter\\w3.txt";
String str = "字符流写测试";
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
FileWriter writer1 = new FileWriter(file1);
for(char ch : chars) {
writer1.write(ch);
}
writer1.flush();
writer1.close();
FileWriter writer2 = new FileWriter(file2);
writer2.write(chars);
writer2.flush();
writer2.close();
FileWriter writer3 = new FileWriter(file3);
writer3.write(str);
writer3.flush();
writer3.close();
}
|
测试结果如下所示:
BufferedReader、BufferedWriter 输入、输出缓冲字符流
正如字节缓冲流BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream一样,Java针对字符流也提供了相应的缓冲类BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
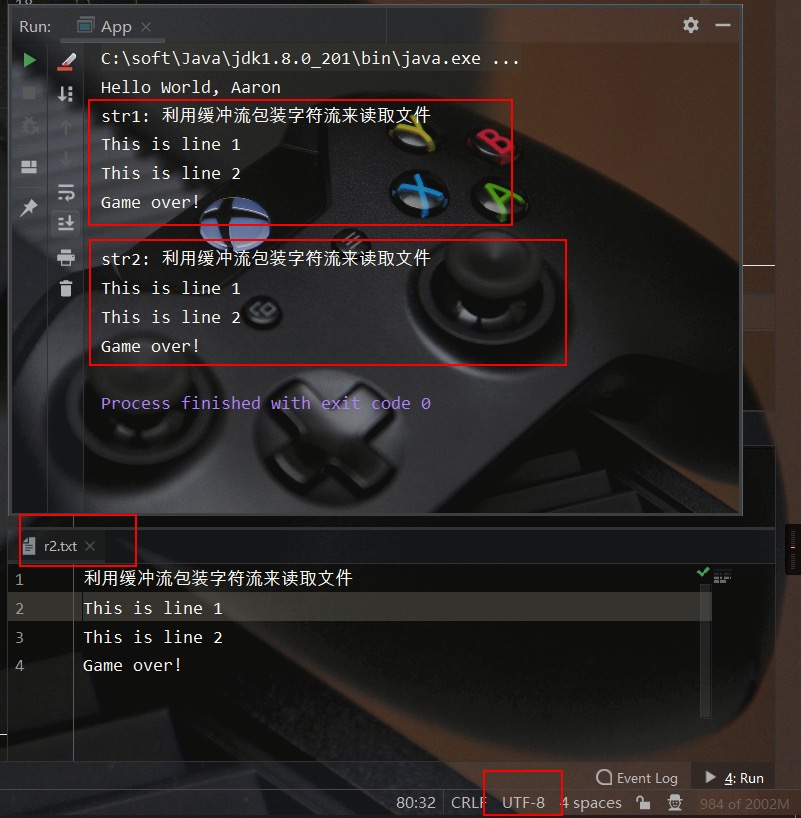
1. BufferedReader 输入缓冲字符流
我们需要先创建一个输入字符流,然后通过BufferedReader进行包装装饰。特别地,在BufferedReader中还提供了一个按行读的readLine方法。其具体用法如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public static void testBufferedReader() throws Exception {
String file = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOBufferTest\\r2.txt";
FileInputStream in = null;
InputStreamReader reader = null;
BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;
in = new FileInputStream(file);
reader = new InputStreamReader(in, "gbk");
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(reader);
String temp = null;
String str = "";
String newLineFlag = System.getProperty("line.separator");
while( (temp=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null ) {
str += temp + newLineFlag;
}
bufferedReader.close();
System.out.println("str1: " + str);
in = new FileInputStream(file);
reader = new InputStreamReader(in, "gbk");
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(reader);
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
int count = -1;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while( (count = bufferedReader.read(buffer))!=-1 ) {
sb.append( buffer,0, count );
}
bufferedReader.close();
System.out.println("str2: " + sb.toString());
}
|
测试文件、测试结果如下所示:
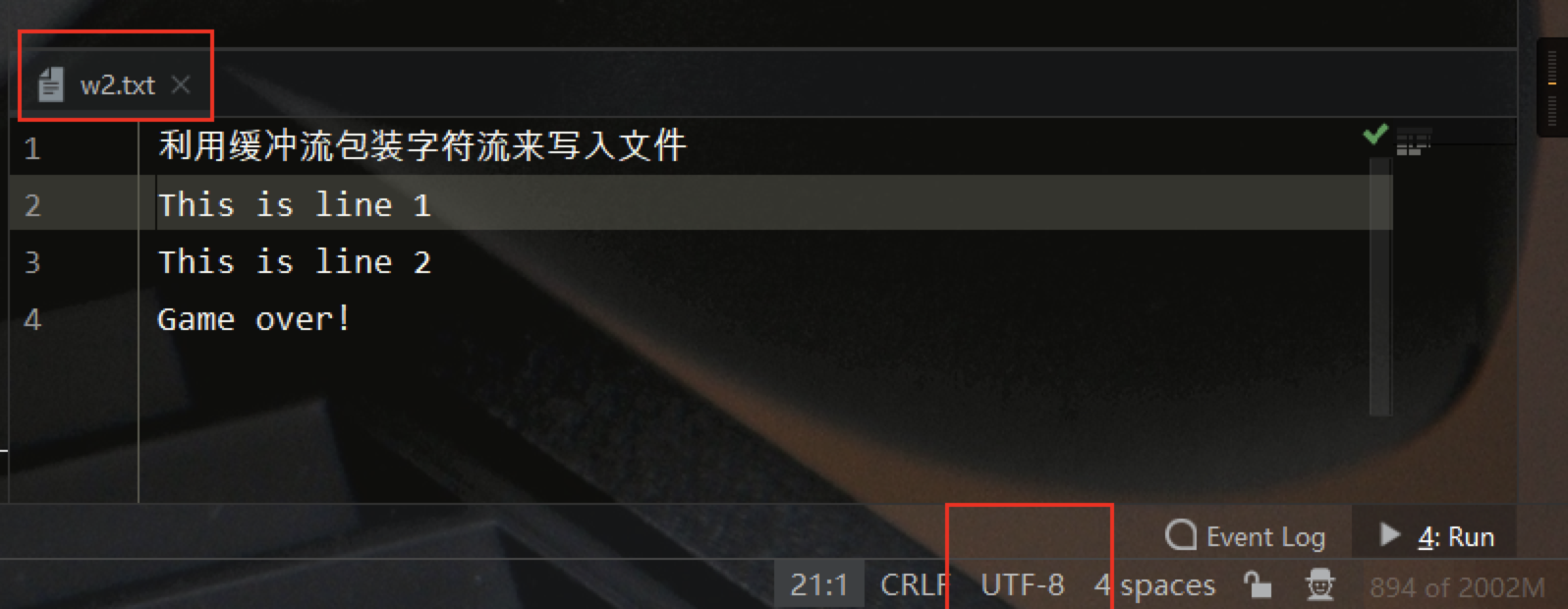
2. BufferedWriter 输出缓冲字符流
同样地,我们需要先创建一个输出字符流,然后通过BufferedWriter进行包装装饰。其具体用法如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public static void testBufferedWriter() throws Exception {
String file = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\IOBufferTest\\w2.txt";
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "gbk");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(writer);
String str = "利用缓冲流包装字符流来写入文件\n"
+ "This is line 1\n"
+ "This is line 2\n"
+ "Game over!";
bufferedWriter.write(str);
bufferedWriter.flush();
bufferedWriter.close();
}
|
测试结果如下所示:
参考文献
- Java核心技术·卷II 凯.S.霍斯特曼著











