Java 8开始支持Lambda表达式,其避免了我们创建匿名内部类的麻烦,形式上更加优雅简洁易读。而如果我们Lambda表达式中只是调用一个已经封装过的方法,则显得过于繁琐、不够简约,为此Java 8在支持Lambda表达式的同时,也提供了一个语法糖:方法引用
方法引用
方法引用有如下4种使用形式:
- 类名::静态方法名
- 对象实例名::实例方法名
- 类名::实例方法名
- 类名::new
类名::静态方法名
对于静态方法,通过类名::静态方法名的方式,即可调用该方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public static void testMethodRef1() {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(-12);
set.add(3);
set.add(-8);
set.add(4);
System.out.println("------------ Lambda Expression ------------");
set.forEach( (e) -> {
MethodRefTest.getNum(e);
} );
System.out.println("\r\n------------ Method Reference ------------");
set.forEach( MethodRefTest::getNum );
}
public static void getNum(Integer a) {
Integer num = Math.abs(a);
System.out.println("num: " + num);
}
|
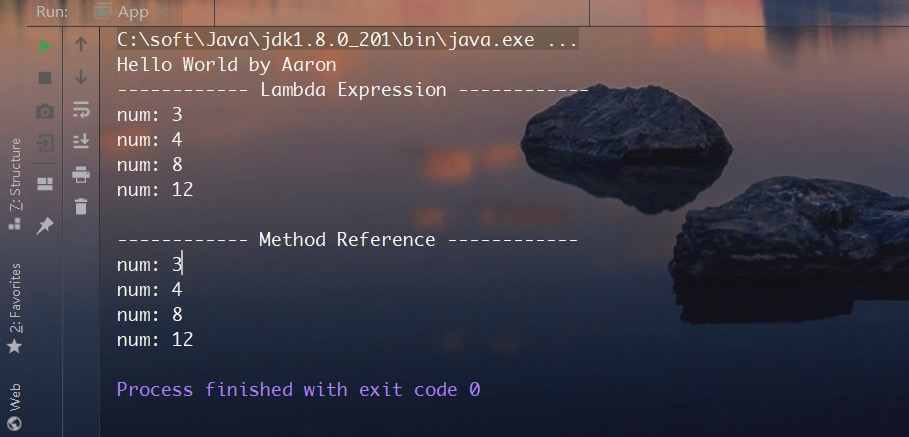
测试结果如下,表明上述两种形式作用是一致的,函数式接口中的参数全部传入所指定的静态方法中
对象实例名::实例方法名
对于实例方法,可以通过 对象实例名::实例方法名 的方式来使用,代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| public class MethodRefTest {
public static void testMethodRef2() {
Set<Student> set = new HashSet<>();
for(int i=0; i<2; i++) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setAge(i);
student.setId(i);
student.setName(String.valueOf(i));
set.add(student);
}
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setName("Aaron");
stu.setId(78);
stu.setAge(24);
System.out.println("------------ Lambda Expression ------------");
set.forEach( (e) -> {
stu.getDetail(e);
} );
System.out.println("\r\n------------ Method Reference ------------");
set.forEach(stu::getDetail);
}
}
@Data
class Student{
private Integer age;
private Integer id;
private String name;
public void getDetail() {
System.out.println("call: " + this);
}
public void getDetail(Student s) {
System.out.println("call: " + this);
System.out.println("param: " + s);
}
}
|
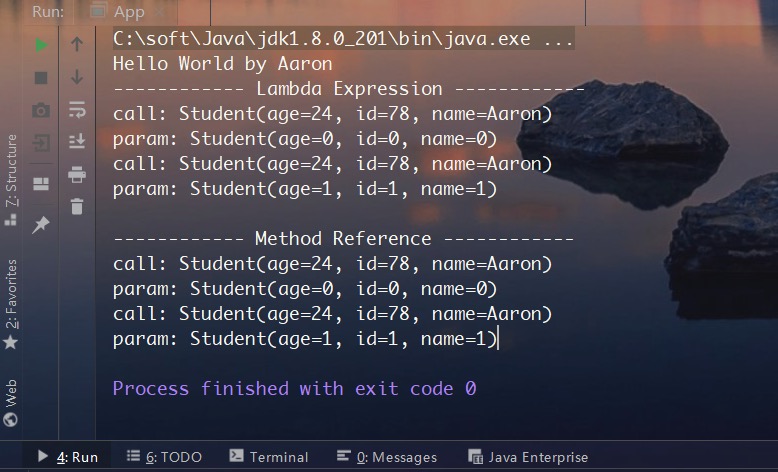
测试结果如下,表明上述两种形式作用是一致的。函数式接口中的参数全部传入所指定的实例方法中,而实例方法的调用者即为在lambda表达式和方法引用中指定的实例对象
类名::实例方法名
对于实例方法,其实还可以通过 类名::实例方法名 的方式来使用,代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| public class MethodRefTest2 {
public static void testMethodRef3() {
Set<Student> set = new HashSet<>();
for(int i=0; i<2; i++) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setAge(i);
student.setId(i);
student.setName(String.valueOf(i));
set.add(student);
}
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setName("Aaron");
stu.setId(78);
stu.setAge(24);
System.out.println("------------ Lambda Expression ------------");
set.forEach( (e) -> {
e.getDetail();
} );
System.out.println("\r\n------------ Method Reference ------------");
set.forEach(Student::getDetail);
}
}
@Data
class Student{
private Integer age;
private Integer id;
private String name;
public void getDetail() {
System.out.println("call: " + this);
}
public void getDetail(Student stu) {
System.out.println("call: " + this);
System.out.println("param: " + stu);
}
}
|
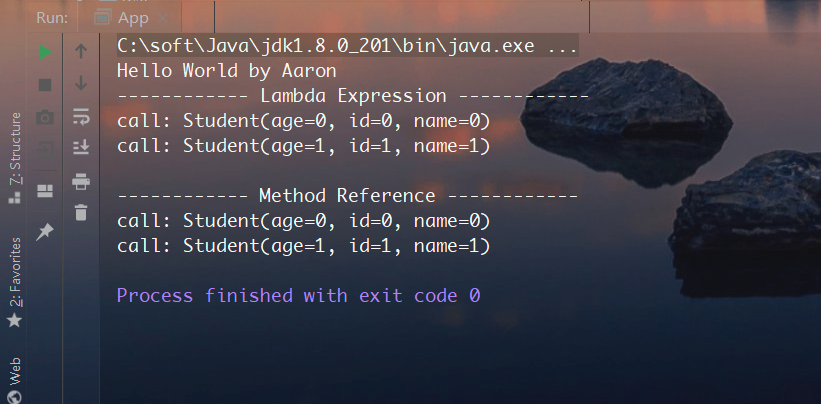
测试结果如下,表明上述两种形式作用是一致的,此时在方法引用中函数式接口所传入的第一个参数即为实例方法的调用者,如果有剩余参数的话,其将全部传入所指定的实例方法中
上述三种方法引用与相应lambda表达式的对应关系,总结如下
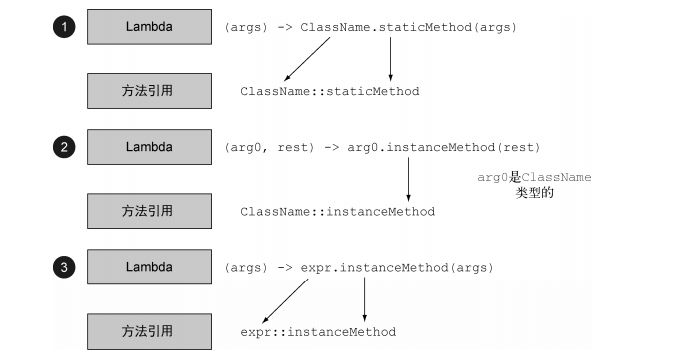
类名::new
对于构造器,可通过 类名::new 的方式来调用,代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public static void testMethodRef4() {
String[] array = new String[]{"Aaron", "Bob", "Tony"};
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(array);
System.out.println("------------ Lambda Expression ------------");
List<Student> students1 = list.stream()
.map(str -> new Student(str) )
.collect(Collectors.toList());
students1.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("------------ Method Reference ------------");
List<Student> students2 = list.stream()
.map(Student::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
students2.forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
class Student{
private Integer age;
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
|
测试结果如下,表明上述两种形式作用是一致的:
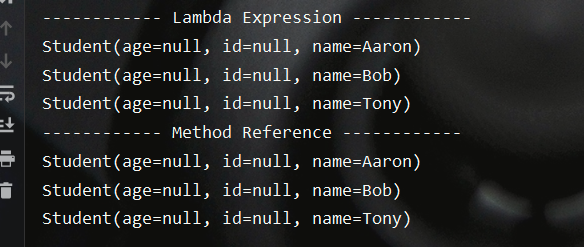
参考文献
- Java实战·第2版 拉乌尔-加布里埃尔·乌尔玛、马里奥·富斯科、艾伦·米克罗夫特著






