虽然像FileOutputStream、OutputStreamWriter这些输出流可以输出信息,但是其会要求把数据先处理为字符串或字节数组,使用不便。为此在Java IO体系专门提供了两个打印流——PrintStream 字节打印流 、PrintWriter 字符打印流。二者均重载了print、printf 等函数,方便开发者直接输出打印其它类型的数据
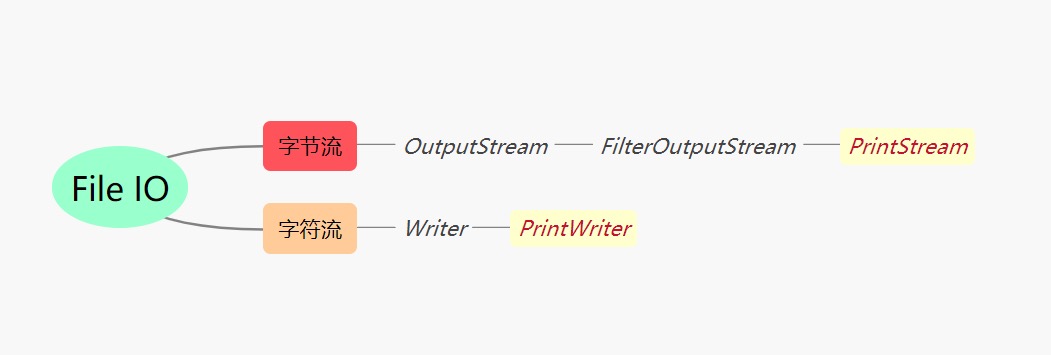
PrintStream 字节打印流
PrintStream其支持多种构造方式,如下所示。值得一提的是PrintStream是对字节输出流的包装,所以即使是从文件中直接创建字节打印流,其构造方法内部也是先构造一个FileOutputStream字节输出流
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class PrintStream extends FilterOutputStream {
...
public PrintStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException;
public PrintStream(File file, String csn) throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException;
public PrintStream(OutputStream out);
public PrintStream(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException;
...
}
|
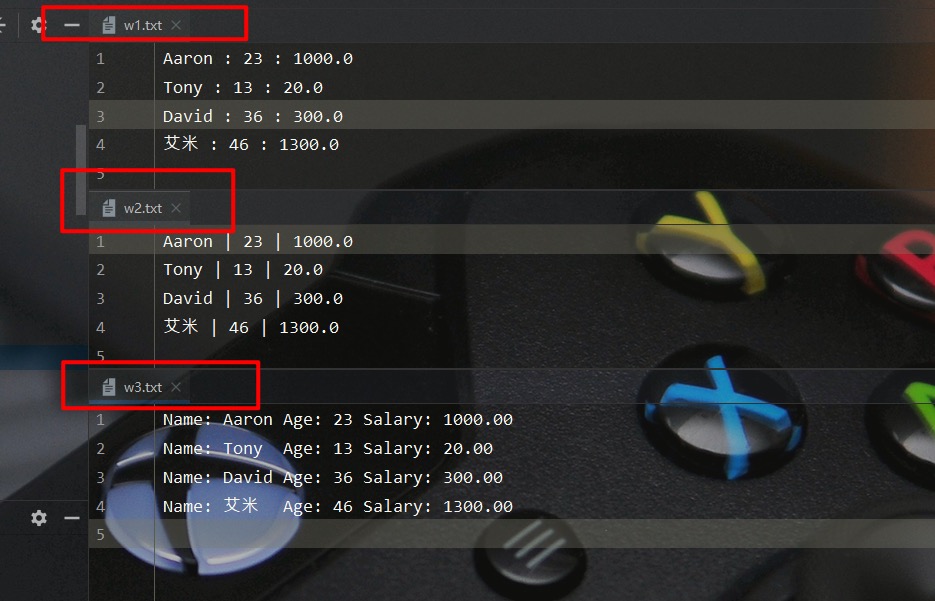
这里一个实例来演示如何通过 PrintStream 字节打印流来直接输出数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
|
public static void testPrintStream() throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
String file1 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\PrintStreamTest\\w1.txt";
String file2 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\PrintStreamTest\\w2.txt";
String file3 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\PrintStreamTest\\w3.txt";
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file1);
PrintStream printStream1 = new PrintStream(out, true, "gbk");
getList().forEach( e -> {
String separator = " : ";
printStream1.print(e.getName());
printStream1.print(separator);
printStream1.print(e.getAge());
printStream1.print(separator);
printStream1.println(e.getSalary());
});
printStream1.flush();
printStream1.close();
PrintStream printStream2 = new PrintStream(file2,"gbk");
getList().forEach( e ->{
String separator = " | ";
printStream2.print(e.getName());
printStream2.print(separator);
printStream2.print(e.getAge());
printStream2.print(separator);
printStream2.println(e.getSalary());
});
printStream2.flush();
printStream2.close();
PrintStream printStream3 = new PrintStream(file3, "gbk");
getList().forEach( e ->
printStream3.printf("Name: %s\tAge: %d\tSalary: %.2f\n",
e.getName(), e.getAge(), e.getSalary())
);
printStream3.flush();
printStream3.close();
}
public static List<Employee> getList() {
Employee e1 = Employee.builder()
.name("Aaron")
.age(23)
.salary(1000.00)
.build();
Employee e2 = Employee.builder()
.name("Tony")
.age(13)
.salary(20.00)
.build();
Employee e3 = Employee.builder()
.name("David")
.age(36)
.salary(300.00)
.build();
Employee e4 = Employee.builder()
.name("艾米")
.age(46)
.salary(1300.00)
.build();
List<Employee> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(e1);
list.add(e2);
list.add(e3);
list.add(e4);
return list;
}
|
从下面的测试结果可以看出,我们不仅可以通过 print、println 方法直接输出打印其它类型的数据,还可以通过printf实现格式化输出
PrintWriter 字符打印流
同样地,PrintWriter 也是对字符输出流的包装,所以虽然其构造函数支持从文件、字节输入流中构造,但是构造函数内部均先构造了一个BufferedWriter实例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class PrintWriter extends Writer {
...
public PrintWriter(File file) throws FileNotFoundException;
public PrintWriter(File file, String csn)
public PrintWriter(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException;
public PrintWriter(OutputStream out);
public PrintWriter (Writer out);
...
}
|
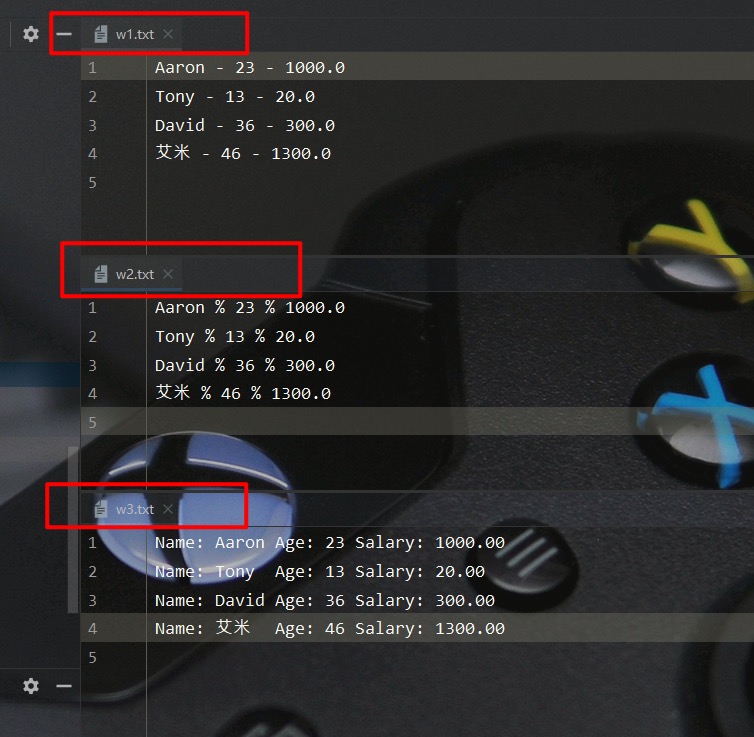
这里一个实例来演示如何通过 PrintWriter 字符打印流来直接输出数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| public static void testPrintWriter() throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
String file1 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\PrintWriterTest\\w1.txt";
String file2 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\PrintWriterTest\\w2.txt";
String file3 = "E:\\TestCode\\JavaTest\\src\\main\\resources\\PrintWriterTest\\w3.txt";
PrintWriter printWriter1 = new PrintWriter(file1,"gbk");
getList().forEach( e -> {
String separator = " - ";
printWriter1.print(e.getName());
printWriter1.print(separator);
printWriter1.print(e.getAge());
printWriter1.print(separator);
printWriter1.println(e.getSalary());
});
printWriter1.flush();
printWriter1.close();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream2 = new FileOutputStream(file2);
PrintWriter printWriter2 = new PrintWriter(fileOutputStream2);
getList().forEach( e -> {
String separator = " % ";
printWriter2.print(e.getName());
printWriter2.print(separator);
printWriter2.print(e.getAge());
printWriter2.print(separator);
printWriter2.println(e.getSalary());
});
printWriter2.flush();
printWriter2.close();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream3 = new FileOutputStream(file3);
OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream3, "gbk");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(outputStreamWriter);
PrintWriter printWriter3 = new PrintWriter(bufferedWriter);
getList().forEach( e ->
printWriter3.printf("Name: %s\tAge: %d\tSalary: %.2f\n",
e.getName(), e.getAge(), e.getSalary())
);
printWriter3.flush();
printWriter3.close();
}
|
可以看出,PrintWriter 与 PrintStream 相比,在输出打印的使用上,并无明显区别
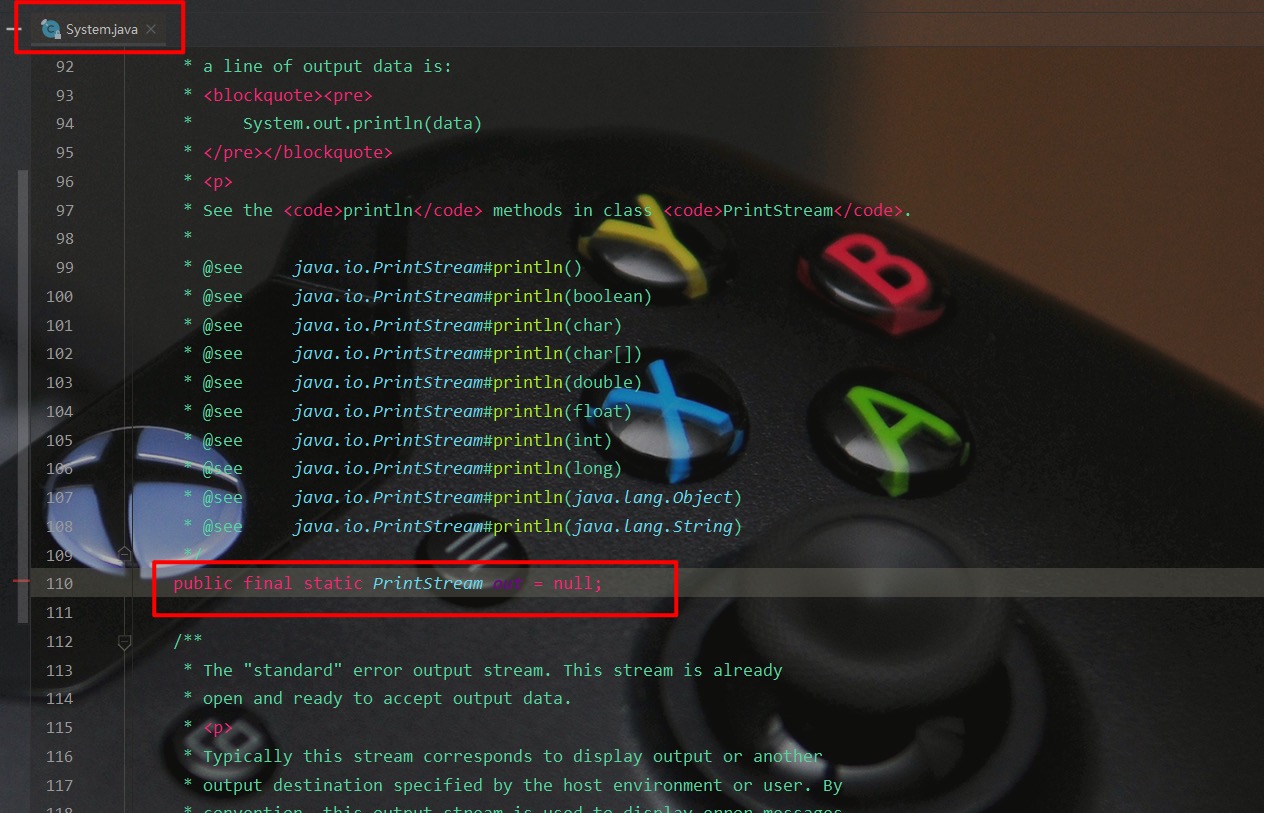
System.out.println
我们在日常开发经常会用 System.out.println 来向控制台打印输出信息,其实 out 就是System类中一个PrintStream类型的静态成员变量
参考文献
- Java核心技术·卷II 凯.S.霍斯特曼著




